The time it takes to charge an electric vehicle (EV) depends on the type of charger you're using, the size of your EV’s battery, and the charging infrastructure available. Here’s an overview of the average charging times by charger type:
1. Level 1 Charger (Standard Home Outlet)
- Charging speed: 2-5 miles of range per hour
- Power: 120V (standard household outlet)
- Typical use: Home charging (if no other option is available)
- Charging time:
- Full charge: 20 to 40 hours for a typical EV with a 60-75 kWh battery.
Details:
A Level 1 charger is simply a standard 120V household outlet. It’s the slowest charging option but is often used for overnight charging at home. It’s typically sufficient for drivers with short daily commutes but impractical for those who need to recharge quickly.
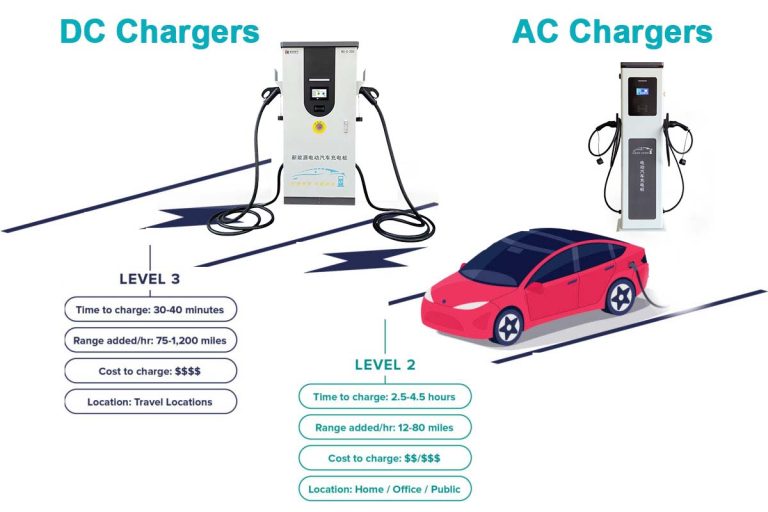
2. Level 2 Charger (Home or Public Charger)
- Charging speed: 10-60 miles of range per hour
- Power: 240V (commonly used in homes and public charging stations)
- Typical use: Home charging (installed by an electrician) or public charging locations like shopping centers, workplaces, etc.
- Charging time:
- Full charge: 4 to 10 hours for a 60-75 kWh battery, depending on the power output of the charger.
Details:
Level 2 chargers are much faster than Level 1 and are widely available both in homes and public locations. They typically provide 10-30 miles of range per hour of charging, meaning a typical full charge could take anywhere from 4 to 10 hours depending on the vehicle's battery size and charger power (usually ranging from 3.3 kW to 22 kW).
3. DC Fast Charger (Level 3 Charger)
- Charging speed: 60-100+ miles of range per 30 minutes
- Power: 400V to 800V DC
- Typical use: Public charging stations along highways, used for long-distance travel.
- Charging time:
- Full charge: 30 minutes to 1 hour for an 80% charge (most EVs stop charging at 80% to protect battery health).
Details:
DC Fast Charging is the fastest way to charge an EV and is typically found in public locations like highway rest stops or high-traffic areas. The time to charge depends on the charger’s power (typically 50 kW to 350 kW) and the vehicle's battery capacity and charging capability. DC Fast Chargers can charge most EVs to 80% in 30 minutes to 1 hour, though the last 20% of charging takes longer.
4. Tesla Supercharger
- Charging speed: 170-200 miles of range per 15 minutes (with V3 Superchargers)
- Power: Up to 250 kW (V3 Supercharger)
- Typical use: Tesla-specific charging stations for long-distance travel.
- Charging time:
- Full charge: 30 to 45 minutes for an 80% charge (Tesla Superchargers generally charge to 80% quickly, then slow down for the final 20%).
Details:
Tesla Superchargers are a proprietary network of DC fast chargers designed for Tesla vehicles, and newer V3 Superchargers are capable of providing up to 250 kW of power. They are incredibly fast and can add 170-200 miles of range in about 15 minutes, but, like other DC fast chargers, the rate slows down after 80% to preserve battery health.
5. Ultra-Fast Chargers (800V System)
- Charging speed: 200-350 miles of range per 15 minutes
- Power: 800V (typically used by high-performance EVs like the Hyundai Ioniq 5, Porsche Taycan)
- Typical use: Public charging stations with high-performance chargers.
- Charging time:
- Full charge: 30 to 45 minutes (for 80% charge)
Details:
These chargers are cutting-edge, using 800V technology to deliver faster charging speeds. They are capable of recharging high-performance EVs like the Porsche Taycan and Hyundai Ioniq 5 from 5% to 80% in under 20-30 minutes.
Charging Time Summary
| Charger Type | Power | Typical Charging Speed | Time for Full Charge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (120V) | 1.4 kW | 2-5 miles per hour | 20-40 hours |
| Level 2 (240V) | 3.3-22 kW | 10-60 miles per hour | 4-10 hours |
| DC Fast Charger (Level 3) | 50-350 kW | 60-100 miles per 30 minutes | 30-60 minutes (80% charge) |
| Tesla Supercharger | 150-250 kW | 170-200 miles per 15 minutes (V3) | 30-45 minutes (80% charge) |
| Ultra-Fast Chargers | 350 kW+ | 200-350 miles per 15 minutes | 30-45 minutes (80% charge) |
Factors Affecting Charging Time:
- Battery size: Larger batteries take longer to charge than smaller ones.
- Charger power: Higher power chargers (e.g., DC fast chargers) charge faster.
- Battery state: Charging typically slows down after 80% to protect the battery health.
- Environmental conditions: Extremely cold or hot temperatures can slow down charging rates.