As electric vehicles (EVs) become more popular, you’ve probably seen terms like "kW" and "kWh" when talking about EV chargers and batteries. These two units—kilowatts (kW) and kilowatt-hours (kWh)—are often used interchangeably by mistake, but they refer to different things. Understanding the difference between kW and kWh is key to making sense of EV charging, so let’s break down what each one really means and how they impact your EV experience.
What is kW (Kilowatt)?
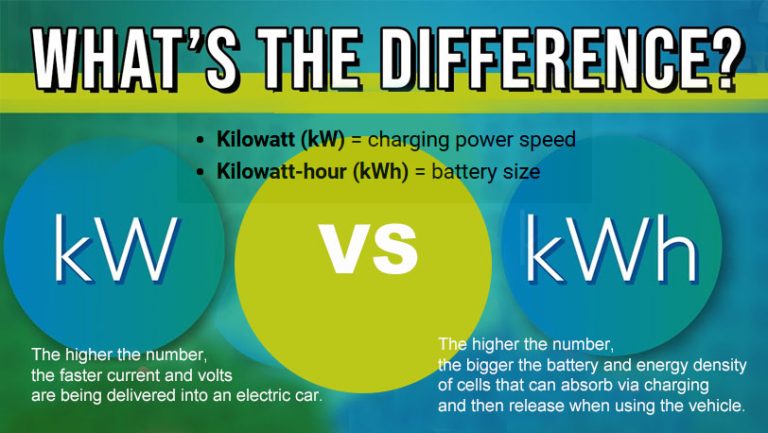
Kilowatt (kW) is a unit of power. Power is the rate at which energy is used or transferred, and in the context of EVs, it’s the speed at which energy flows from the charger to your car’s battery. In simpler terms, kW tells you how fast your EV can charge.
When you see a charger rated at 50 kW or 150 kW, that number tells you the maximum charging speed that charger can deliver at any moment, assuming your EV can handle that rate. Just like a water hose with a larger diameter will fill a pool faster, a higher kW rating means faster charging.
For example:
A 7 kW charger is considered "slow" and is often used for home charging.
A 120 kW charger is "fast" and typical for public charging stations.
A 240 kW charger or higher is "ultra-fast," found mainly in dedicated fast-charging networks.
It’s worth noting that EVs themselves have a limit on how much power they can take. So even if you plug into a 160 kW charger, if your car can only accept 60 kW, that’s the maximum speed at which it will charge.
What is kWh (Kilowatt-hour)?
Kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a unit of energy. While power measures speed, energy measures quantity—how much energy is stored or transferred over time. For EVs, kWh is used to represent the capacity of the battery.
Think of kWh as the size of your car’s fuel tank. A car with a 60 kWh battery pack can store more energy than one with a 40 kWh battery pack, meaning it can drive further on a single charge.
For instance:
If your EV has a 60 kWh battery, it can theoretically run for 60 hours on 1 kW of power (though actual driving time depends on many factors, including speed, terrain, and weather).
When you charge your EV, the charger is transferring kWh of energy to refill your battery’s storage.
How Do kW and kWh Work Together in EV Charging?
To understand how these two units work together, let’s look at an example. Suppose you have an EV with a 70 kWh battery and you plug it into a 22kW charger. To calculate how long it will take to fully charge, divide the battery’s kWh capacity by the charger’s kW output:
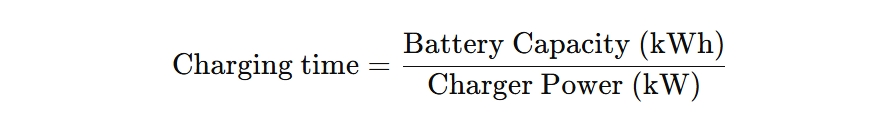
So, a 70 kWh battery on a 22kW charger would take about 3.2 hours to charge from empty to full.
Why Does the Difference Matter?
Understanding the distinction between kW and kWh can help you make informed decisions about EV charging. Here’s why it’s useful to know:
- Choosing the Right Charger for Your Needs: For home use, a slower charger (like a 7 kW) may be sufficient because you can charge overnight. But if you frequently take long trips and need quick top-ups, a fast or ultra-fast public charger (60+ kW) might be essential for your routine.
- Estimating Charging Times: Knowing the battery’s kWh capacity and the charger’s kW output allows you to estimate how long it will take to reach a full charge. This helps you plan your time efficiently, especially when using public chargers.
- Managing Range Expectations: A larger battery capacity (higher kWh) means a longer range between charges. However, it also means it will take longer to charge fully, even on a fast charger, compared to a smaller battery.
- Understanding EV Capabilities: Just because a charger is rated at a high kW doesn’t mean every EV can charge at that speed. Knowing your EV’s maximum charge rate helps you avoid overestimating how quickly you can recharge.
kW (kilowatts): A measure of power that indicates how fast energy flows from the charger to the EV battery.
kWh (kilowatt-hours): A measure of energy that represents the total amount of energy the battery can hold or the total amount transferred during charging.
So, next time you see kW and kWh mentioned, you’ll know: kW tells you the speed of charging, while kWh tells you the amount of energy in your battery. With this knowledge, you can better navigate EV charging options, estimate charging times, and make the most out of your EV experience!