When it comes to electric vehicle (EV) charging, there are two types of charging available: AC and DC. Both methods of charging have their own unique advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we'll explore the differences between these two types of charging and how they impact the charging experience for EV owners.
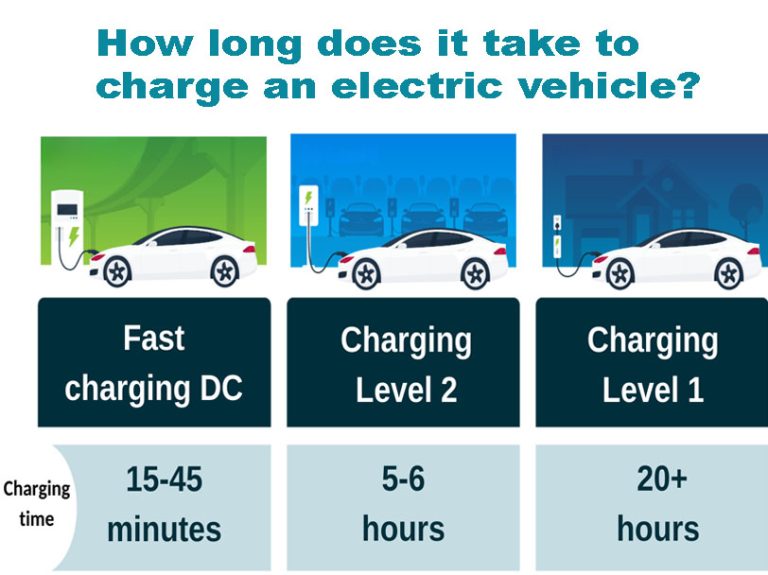
AC charging, or Level 2 charging, is the more common and widely used method of charging for EVs. AC charging is done by plugging the vehicle into an AC charging station that uses a standard 240-volt power source. These charging stations are typically found at homes, offices, and public locations such as shopping centers and parking garages.
One of the main advantages of AC charging is that it is much cheaper than DC charging. In addition, Level 2 chargers are far more ubiquitous and easy to find than Level 3 chargers, meaning that it is much more convenient for EV owners to charge their cars using AC charging.



DC charging, or Level 3 charging, is a much faster and more powerful method of charging than AC charging. DC charging is typically found at public charging stations and uses a direct current (DC) power source to charge the batteries directly instead of using an AC-DC converter intermediary.
One of the biggest advantages of DC charging is its speed. Level 3 chargers can fully charge an EV battery in as little as 30 minutes, making it much more practical for long-distance trips or when time is of the essence. However, the cost of installing and operating Level 3 chargers is significantly higher than Level 2 chargers.