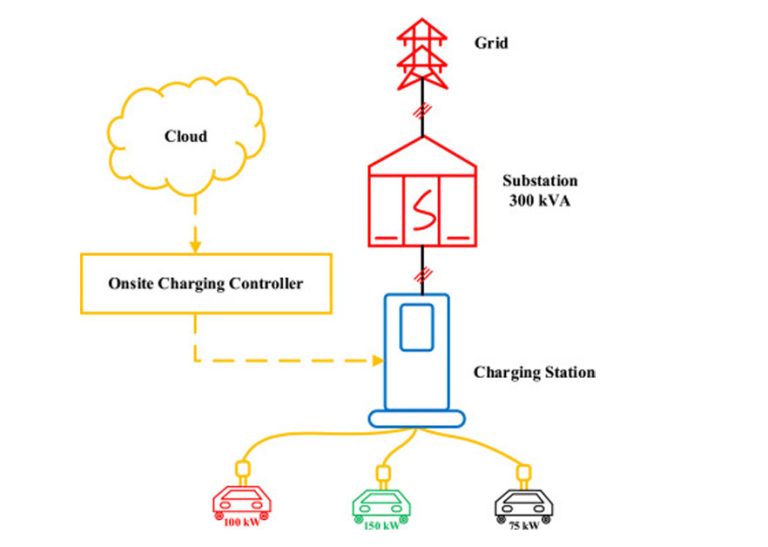
As the EV market grows, governments worldwide are introducing new regulations to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles and ensure robust charging infrastructure. In 2024, several key regulations are set to reshape the EV charging landscape, impacting manufacturers, businesses, and EV drivers alike. Here’s what you need to know about these changes and how they might affect you.
1. Mandatory Charging Infrastructure in New Buildings
Many countries are implementing regulations that require new residential and commercial buildings to include EV charging infrastructure.
- Europe: The EU mandates that all new buildings and major renovations include pre-wiring for EV chargers, with larger buildings required to have functional chargers installed.
- United States: States like California are introducing similar requirements for residential and commercial construction.
This regulation ensures that EV drivers have convenient access to chargers at home and work, supporting EV adoption.
2. Minimum Standards for Public Chargers
Governments are setting minimum standards for public EV chargers to improve reliability and user experience.
- Uptime Requirements: In the U.S., the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) program mandates a 97% uptime for federally funded chargers.
- Universal Payment Options: Public chargers must support multiple payment methods, such as credit cards and mobile apps.
- Accessibility: New rules require charging stations to meet accessibility standards for all users.
These regulations aim to eliminate frustration caused by unreliable or difficult-to-use charging networks.
3. Stricter Interoperability Standards
Interoperability is becoming a priority as governments push for seamless charging across networks.
- Connector Compatibility: EV chargers must support multiple connector types, such as CCS, CHAdeMO, and Tesla adapters, to accommodate various EV models.
- Cross-Network Access: New regulations encourage or require charging networks to allow access via a single subscription or roaming agreements, simplifying the process for EV drivers.
This ensures EV drivers can charge their vehicles without being locked into a single network.
4. Increased Renewable Energy Integration
Governments are emphasizing the integration of renewable energy sources into EV charging.
- Europe: The EU’s Green Deal promotes solar-powered chargers and grid balancing to enhance sustainability.
- United States: Federal incentives prioritize chargers powered by renewable energy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
These measures align EV charging infrastructure with global sustainability goals.
5. Funding for Rural and Underserved Areas
In 2024, governments are focusing on closing the gap in charging infrastructure in rural and underserved regions.
- United States: NEVI funds are allocated to expand EV chargers along highways and in rural communities.
- Global Trends: Similar programs are being launched in India, Australia, and parts of Africa to increase EV adoption in less accessible areas.
This ensures equitable access to EV charging, regardless of location.
6. Carbon Credit Programs for EV Charging
New and updated carbon credit programs incentivize businesses and individuals to install EV chargers.
- California’s LCFS (Low Carbon Fuel Standard): Offers credits to businesses that install and operate EV chargers.
- EU’s Emissions Trading System: Expands to include EV infrastructure as part of carbon offset opportunities.
These programs provide financial benefits for those investing in EV charging infrastructure.
How These Regulations Impact Businesses and EV Owners
For Businesses:
- Opportunities to receive funding and tax incentives for installing chargers.
- The need to comply with new standards for public chargers.
- Enhanced customer attraction by meeting regulatory requirements and supporting sustainability goals.
For EV Owners:
- Improved access to reliable, user-friendly charging stations.
- Expanded charging options in rural and underserved areas.
- Greater confidence in transitioning to EVs, thanks to increased infrastructure availability.