Electric vehicle charging station play a crucial role in the operation of electric vehicles. Understanding their working principle can provide us with a better comprehension of how these devices enable the charging process.
Basic Components of a Charging Pile
A charging pile generally consists of several key components. First, there is the power conversion module. This part is responsible for converting the input power from the grid into the appropriate voltage and current levels required by the electric vehicle's battery. It may include transformers, rectifiers, and other power - handling components.
Secondly, there is the control unit. The control unit acts as the "brain" of the charging pile. It monitors and controls the charging process. It communicates with the electric vehicle's battery management system (BMS) to obtain information such as the battery's state of charge, temperature, and voltage. Based on this information, it adjusts the charging parameters to ensure safe and efficient charging.
There are also connection interfaces. These include the plug and socket that physically connect the charging pile to the electric vehicle. Different types of electric vehicles may have different types of charging interfaces, such as the CCS (Combined Charging System), CHAdeMO, or Type 2 connectors, depending on the vehicle's make and model and the charging standard adopted.
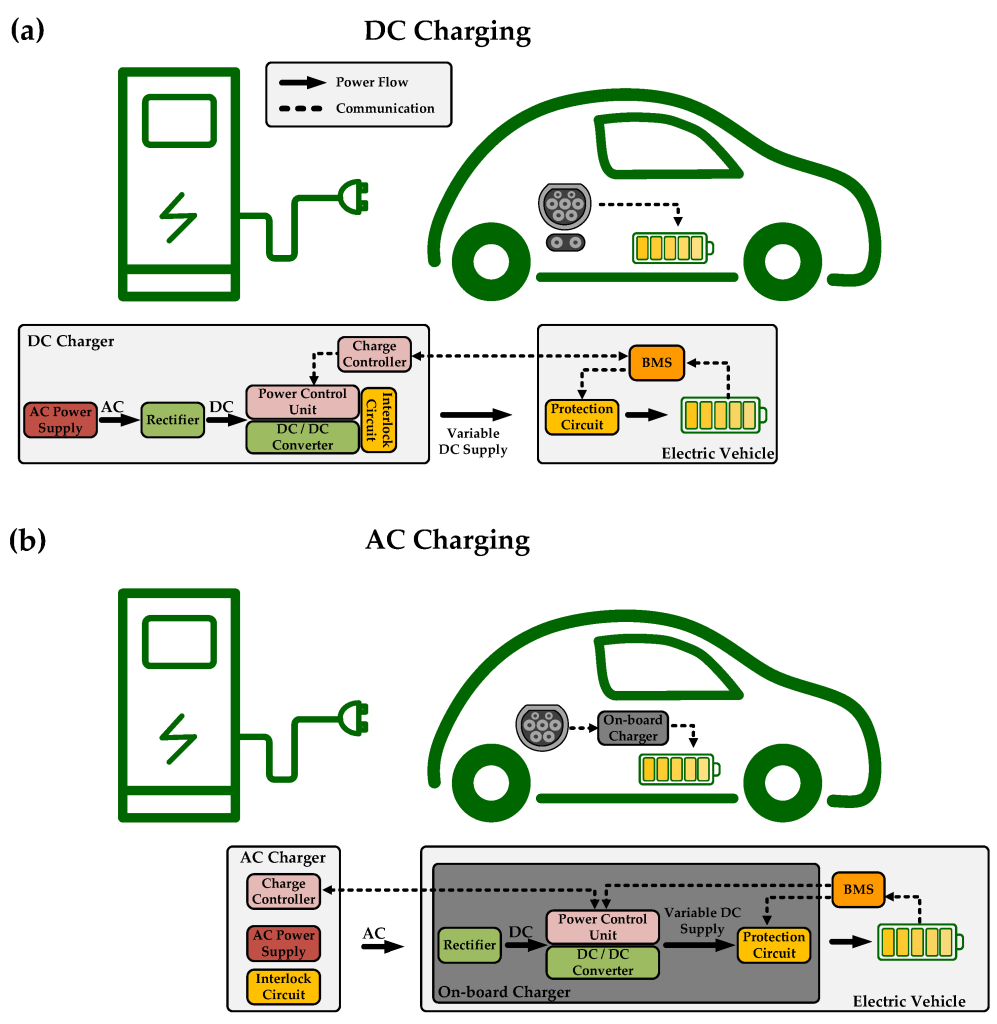
Charging Modes and Their Principles
AC Charging: In AC (alternating current) charging mode, the charging pile supplies alternating current to the vehicle. The on - board charger in the electric vehicle then converts this AC power into direct current (DC) to charge the battery. The charging speed in AC mode is relatively slower compared to DC charging. The charging pile in AC mode mainly provides the appropriate voltage and current levels based on the vehicle's requirements. For example, in a common household charging situation with a lower power AC charging pile, the voltage might be around 220 volts or 110 volts depending on the local power supply standard, and the current is adjusted within a certain range suitable for the vehicle's on - board charger capacity.



DC Charging: DC charging is a faster charging method. In this case, the charging pile itself converts the alternating current from the grid into direct current and directly supplies it to the vehicle's battery. This bypasses the vehicle's on - board charger. High - power DC charging piles can provide a large amount of current and voltage to quickly charge the battery. For instance, some fast - charging DC piles can deliver hundreds of volts and several hundred amperes of current, enabling the battery to be charged to a significant level in a short time. However, DC charging requires more advanced power conversion and control technology in the charging pile to ensure the safety and stability of the charging process, as high - power DC can cause more significant impacts on the battery if not properly controlled.



Communication between the Charging Pile and the Vehicle
During the charging process, effective communication between the charging pile and the electric vehicle is essential. As mentioned earlier, the control unit of the charging pile and the vehicle's BMS communicate with each other. They use specific communication protocols to exchange information. This communication allows the charging pile to know the battery's status and adjust the charging parameters accordingly. For example, if the battery temperature is getting too high during charging, the BMS will send a signal to the charging pile, and the charging pile will adjust the charging current or even stop the charging process to prevent damage to the battery.
In addition, the communication also enables functions such as authentication. When a vehicle is connected to a charging pile, the charging pile may verify the vehicle's identity to ensure that only authorized vehicles can use the charging service. This helps in managing the charging infrastructure and preventing unauthorized use.
Safety Mechanisms in the Charging Process
Safety is of utmost importance in the operation of charging piles. There are several safety mechanisms built into the charging pile system. One of the main safety features is over - current protection. If the current during the charging process exceeds a certain safe value, the charging pile will automatically cut off the power supply to prevent damage to the battery and the charging equipment.
Over - voltage protection is also crucial. Excessive voltage can cause the battery to overcharge, leading to potential safety hazards such as battery swelling, leakage, or even explosion. The charging pile monitors the voltage during charging and takes appropriate action if the voltage exceeds the safe limit.
Leakage protection is another important safety measure. It detects any leakage of current to the ground and shuts down the charging process if a leakage is detected. This protects users from electric shock hazards.
the working principle of electric vehicle charging piles involves a combination of power conversion, control, communication, and safety mechanisms. These elements work together to ensure the safe and efficient charging of electric vehicle batteries, enabling the growth and widespread use of electric vehicles in our daily lives.








