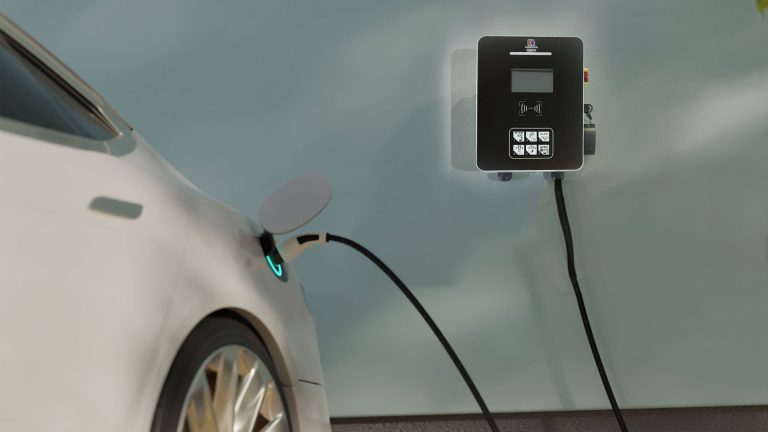
Mastering the secret of charging time can not only improve charging efficiency, but also enhance the overall driving experience. This article will analyze the charging time of electric vehicle charging stations in detail to help car owners better understand and use charging facilities.

1. Basic knowledge of electric vehicle charging
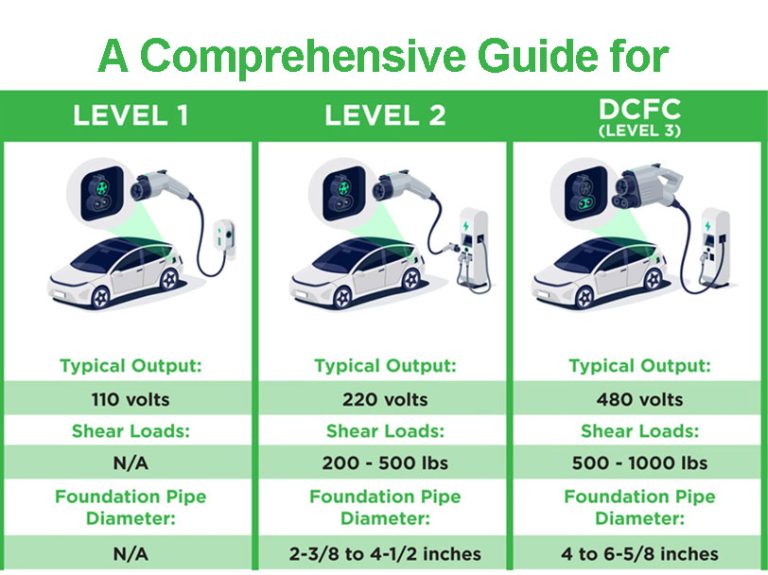
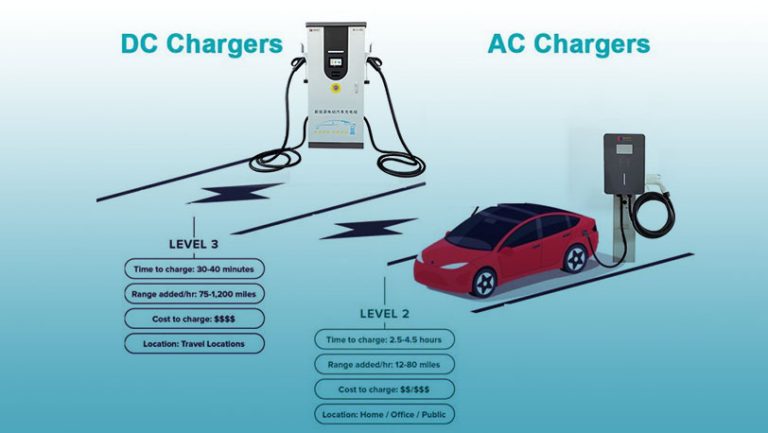
There are three main ways to charge an electric vehicle: slow charging, fast charging, and ultra-fast charging. Each charging method takes a different amount of time and uses different equipment and voltage.
| Type | Level 1 Charging | Level 2 Charging | DC Fast Charging |
| Features | Regular household power socket with a voltage of 120V | Single phase voltage 220V | Three phase 380V or 400v |
| Application | Suitable for home use, mainly for charging at night | Suitable for charging during short stops, such as when shopping | Suitable for long-distance travel and when you need to quickly replenish power |
| Charging Time | Slow charging takes a long time. 8-12 hours to fully charge the battery. | 3~4 hour to be fully charged from 20% to 80%. | 80% of the battery can be charged in 30 minutes |
2. Factors Affecting Charging Time
Although we have understood the basics of different charging methods, the length of charging time is still affected by many factors. The following are the main factors affecting charging time:
1. Battery capacity:
The larger the battery capacity, the longer it takes to charge. For example, an electric car with a 100kWh battery will take significantly different time to fully charge than an electric car with a 40kWh battery.
2. Charging station equipment:
Different brands and models of charging stations have different output powers, which will directly affect the charging speed. For example, some high-power ultra-fast charging stations can provide an output power of 300kW, while the output power of standard fast charging stations usually ranges from 7.2kW to 22kW.
3. Vehicle charging reception capability:
Not all electric vehicles can support all types of charging facilities. If the vehicle can only receive a maximum charging power of 50kW, then even if it is connected to a 100kW charging station, the actual charging speed is still limited.
4. Environmental factors:
External environmental factors such as temperature can also affect charging time. Lithium-ion batteries charge less efficiently at lower temperatures, so charging times for electric vehicles may be lengthened during cold winter months.
5. Grid load:
During peak hours, charging speed may be affected due to increased load on the grid. Some charging stations limit charging power during peak periods to protect the stability of the power system.